
The atomic number density (N atoms/cm 3) of a pure material having atomic or molecular weight (M grams/mol) and the material density (⍴ gram/cm 3) is easily computed from the following equation using Avogadro’s number ( N A = 6.022×10 23 atoms or molecules per mole): The atomic number density (N atoms/cm 3), which is associated with atomic radii, is the number of atoms of a given type per unit volume (V cm 3) of the material. Therefore it is determined by the mass number (number of protons and neutrons). The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about 10 -12 of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge and at least 99.95% of the total mass of the atom. Since the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided by the total volume (V) occupied by that substance, it is obvious, the density of a substance strongly depends on its atomic mass and also on the atomic number density (N atoms/cm 3),
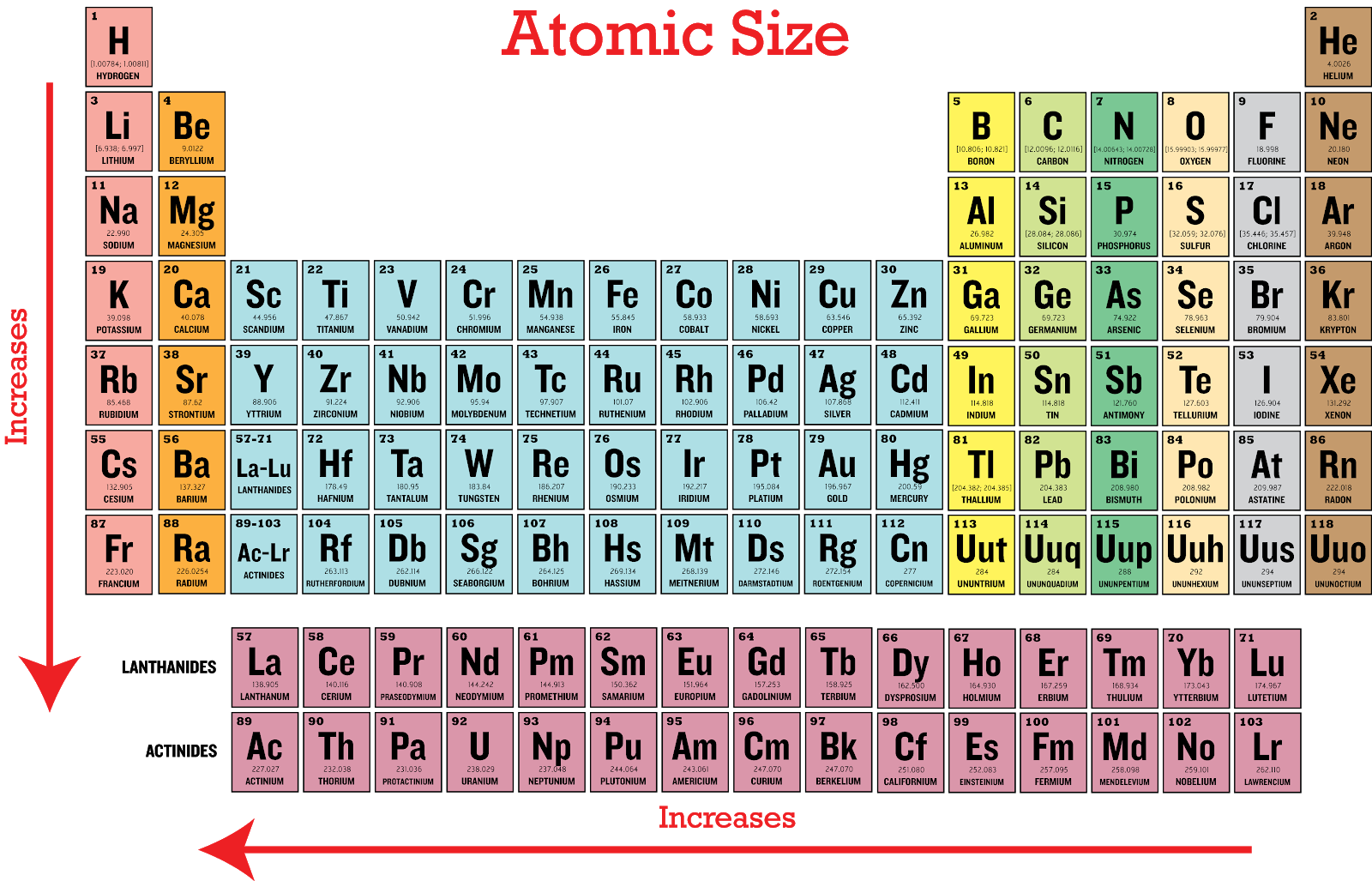
The Standard English unit is pounds mass per cubic foot ( lbm/ft 3). The standard SI unit is kilograms per cubic meter ( kg/m 3). In words, the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided by the total volume (V) occupied by that substance. It is an intensive property, which is mathematically defined as mass divided by volume: Typical densities of various substances are at atmospheric pressure.ĭensity is defined as the mass per unit volume. Therefore the space in an atom (between electrons and an atomic nucleus) is not empty, but it is filled by a probability density function of electrons (usually known as “ electron cloud“). Particle locations in quantum mechanics are not at an exact position, they are described by a probability density function. On the atomic scale, physicists have found that quantum mechanics describes things very well on that scale. The classical description cannot be used to describe things on the atomic scale. Due to the quantum nature of electrons, the electrons are not point particles, they are smeared out over the whole atom. It may seem, that the space and in fact the matter is empty, but it is not. These electrons together weigh only a fraction (let say 0.05%) of entire atom. But this “huge” space is occupied primarily by electrons, because the nucleus occupies only about 1721×10 −45 m 3 of space. Assuming spherical shape, the uranium atom have volume of about 26.9 ×10 −30 m 3. The Van der Waals radius, r w, of an atom is the radius of an imaginary hard sphere representing the distance of closest approach for another atom. For uranium atom, the Van der Waals radius is about 186 pm = 1.86 ×10 −10m. The volume of an atom is about 15 orders of magnitude larger than the volume of a nucleus. As a result, the electron cloud contracts and the atomic radius decreases. Therefore, the effective nuclear charge towards the outermost electrons increases, drawing the outermost electrons closer. The atomic radii decrease across the periodic table because as the atomic number increases, the number of protons increases across the period, but the extra electrons are only added to the same quantum shell.

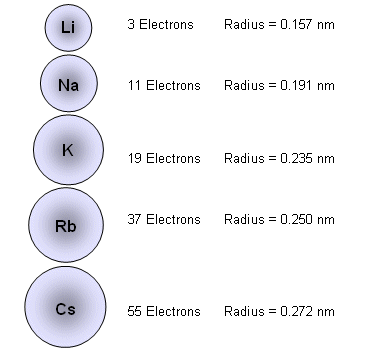
Consequently, the smallest atom is helium with a radius of 32 pm, while one of the largest is caesium at 225 pm. On the periodic table of the elements, atomic radius tends to increase when moving down columns, but decrease when moving across rows (left to right). A metallic radius is one-half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a crystalline structure, when joined to other atoms by metallic bonds. Covalent radius is the nominal radius of the atoms of an element when covalently bound to other atoms. An ionic radius is one-half the distance between the nuclei of two ions in an ionic bond.
K ATOMIC RADIUS FREE
However, this assumes the atom to exhibit a spherical shape, which is only obeyed for atoms in vacuum or free space. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus. It must be noted, atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary. The atomic radius of Potassium atom is 203pm (covalent radius).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
